All programs, instructions, and data must be stored in system memory (RAM) before the computer can use it. It will hold recently used programs, instructions, and data in memory if there is room. The more memory (capacity) in a PC, the more data can hold and the better your computer will perform.
If your computer doesn't have enough memory installed, its CPU must constantly retrieve data from permanent storage (hard disk). This method of data retrieval is slower than retrieving instructions and data from memory. In fact, if your PC doesn't have enough memory, some programs will run very slowly (or you might experience system crashes), and other programs won't run at all!
Here is the graphical illustration of a desktop RAM (left) and laptop RAM (right)
RAM Brand There are a lot of brands, for example Kingston, Apacer, Corsair, Kingmax, etc. Most of the manufacturer offers life time warranty means that whenever the RAM manufacturers still produce the kind of RAM, the warranty is still valid.
RAM Capacity
Memory is measured in terms of bytes. One byte is equal to approximately one character in a word processing document. A unit equaling approximately one thousand bytes (1,024, to be exact) is called a kilobyte (KB), and a unit of approximately one thousand (1,024) kilobytes is called a megabyte (MB). A thousand megabytes is a gigabyte (GB).
The capacity of one piece of RAM ranges from 2 MB to 8 GB (8,000 MB) or whatever latest. Currently, most of the computers are using 512MB, 1 GB, 2 GB, or 4 GB of RAM.
Types of RAM
Before you buy new memory for your computer, it's essential to identify the type you need. The table below lists the RAM modules:
| Name | Number of Notches in Card Edge Connector | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 30-pin SIMM (single inline memory module) | One | Desktop computers (most earlier 286, 386, 486, Pentium I) |
| 72-pin SIMM | One | EDO RAM in desktop computers (mostly Pentium I) |
| 168-pin DIMM (dual inline memory module) | Two | SDRAM in desktop computers (mostly Pentium II and III) |
| 184-pin DIMM | One | DDR SDRAM in desktop computers |
| 184-pin RIMM | Two | Rambus in desktop computers |
| 240-pin DIMM | One | DDR2 SDRAM in desktop computers |
| 240-pin DIMM | One | DDR3 SDRAM in desktop computers |
| 144-pin SODIMM (small outline dual inline memory module) | One | Notebook computers |
| 200-pin SODIMM | One | Notebook computers |
Each memory modules come in a confusing number of different physical sizes, speeds, and other characteristics. Below shows the relative sizes, shapes, and speed of several module types.
1) Types of 72 pins RAM
EDO (Extended Data Output) - Access Speed: 50, 60, 70 nanoseconds
FPM (Fast Page Mode) - Access Speed: 50, 60, 70 nanoseconds
2) Types of 168 pins RAM
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM)
| Memory | Speed (MHz) | Max Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|
| PC 66 | 66 | 0.53 GB/second |
| PC 100 | 100 | 0.80 GB/second |
| PC 133 | 133 | 1.06 GB/second |
| PC 150 | 150 | 1.20 GB/second |
| PC 166 | 166 | 1.20 GB/second |
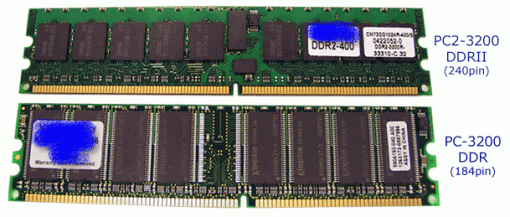
3) Types of 184 pins RAM
DDR (Double Data Rate) SDRAM
| Memory | Speed (MHz) | Max Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|
| PC2100 (DDR 266) | 133 | 2.13 GB/second |
| PC2700 (DDR 333) | 166 | 2.66 GB/second |
| PC3200 (DDR 400) | 200 | 3.20 GB/second |
4) Types of 240 pins RAM DDR2 (Double Data Rate 2) SDRAM
DDR2 400 MHz (PC2-3200)
DDR2 533 MHz (PC2-4200)
DDR2 667 MHz (PC2-5400)
DDR2 800 MHz (PC2-6400)
DDR2 900 MHz (PC2-7200)
DDR2 1000 MHz (PC2-8000)
DDR2 1066 MHz (PC2-8500)
DDR2 1150 MHz (PC2-9200)
DDR2 1200 MHz (PC2-9600)
DDR3 (Double Data Rate 3) SDRAM
DDR3 1066 MHz (PC3-8500)
DDR3 1333 MHz (PC3-10600/10666)
DDR3 1375 MHz (PC3-11000)
DDR3 1600 MHz (PC3-12800)
DDR3 1625 MHz (PC3-13000)
DDR3 1800 MHz (PC3-14400)
DDR3 1866 MHz (PC3-15000)
DDR3 2000 MHz (PC3-16000)
Here are the graphical illustrations between DDR2 and DDR3 desktop RAM
5) Types of 200 pins RAM DDR PC2100 200-pin SODIMM (Small Outline DIMM)
DDR PC2700 200-pin SODIMM
DDR PC3200 200-pin SODIMM
DDR PC4200 200-pin SODIMM
DDR PC5300 200-pin SODIMM
As you can see, the RAM manufacturers is producing more and more advanced RAM in term of RAM capacity and speed. I hope this tutorial will answer your question on what is RAM, the RAM capacity and brand as well as different types of RAM....