Normally, when you buy a CPU it is in a box. Inside the box contains the CPU, heat sink and CPU fan. The followings are the pictures of Intel CPU (left), AMD CPU (middle), and heat sink & fan(right).
CPU Brand: Intel and AMD. The two major manufacturers of CPUs for personal computers are Intel and AMD. Then, people always ask, which is better? The truth is that most users won't see any difference between the two because both of them are more or less same. And since both companies introduce faster versions of most of their CPU models several times a year, this month's performance leader will be a mid-range version a year from now.
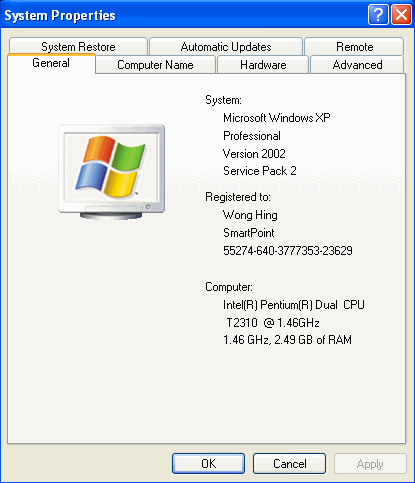
To see which CPU is installed in your system, go to the Windows System Properties utility. If your computer is running Windows XP, all you have to do is follow these steps:
- On the computer desktop, right-click My Computer and choose Properties.
- From the System Properties dialog box displayed, click the General tab.
- The System: section of this dialog box tells you which version of Windows you're running;
- The Registered to: section tells you who you are (or, rather, how your version of Windows is registered);
- The Computer: section tells which type of processor and how much memory (RAM) you have installed.
| Manufacturer | Processor Type | Recommended Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Intel | Celeron | Basic computing," e-mail, home computers* |
| Celeron M | Laptop (notebook) computers | |
| Celeron D | "Value-priced PCs"* | |
| Pentium 4 | Digital home and office applications"* Image processing, games and multimedia | |
| Pentium M | High performance laptop computers | |
| Pentium D (Dual-core) | Multimedia entertainment, digital photo editing, running multiple applications, supporting multiple users | |
| Core Solo | Very-high-performance laptop computers | |
| Core Duo (Dual-core) | "Multiple demanding applications such as graphics-intensive games or serious number-crunching programs-while downloading music or running security programs in the background."* | |
| Core 2 Duo | High-performance energy-efficient desktop and mobile computers | |
| Xeon | Business applications, including Application servers, e-mail servers, Internet servers | |
| Itanium | "Business-critical computing … with mainframe-class reliability"* | |
| AMD | Sempron | "Everyday computing with built-in security"* |
| Athlon 64 | "Leading edge performance with simultaneous 32-bit and 64-bit computing"* | |
| Athlon 64 X2 Dual Core | Running multiple applications simultaneously | |
| Athlon 64 FX | Running "the next generation of digital media and games"* | |
| Turion 64 | "Optimized to deliver AMD64 performance in thinner and lighter notebook PCs"* | |
| Turion 64 X2 | Multi-tasking, long battery life and compatibility with wireless and graphics technologies in high-performance laptops | |
| Opteron (multi-core) | Servers and workstations running simultaneous 32- and 64-bit computing |
CPU Speed
The speed of CPU is measured by frequency in Megahertz (MHz) or Gigahertz (GHz) with 1 GHz equals to 1000 MHz.
Example: 1.0GHz, 1.1 GHz, 1.13 GHz, 1.2 GHz, 1.3 GHz, 1.4 GHz, 1.5 GHz, 1.6 GHz, 1.7GHz, 1.8GHz, 1.9 GHz 2.0 GHz, 2.1 GHz, 2.2 GHz, 2.3 GHz, 2.4GHz, 2.53GHz, 2.6GHz, 2.8GHz, 3.0GHz, 3.2GHz, 3.4GHz, 3.6GHz or whatever latest.
As a conclusion, you should be able to answer the question - What is CPU? - The core component of your computer's operation. Everything else -disk drives, keyboard, mouse, monitor, and Internet connection, among others -is there either to provide instructions to the CPU, respond to data from the CPU, or both.